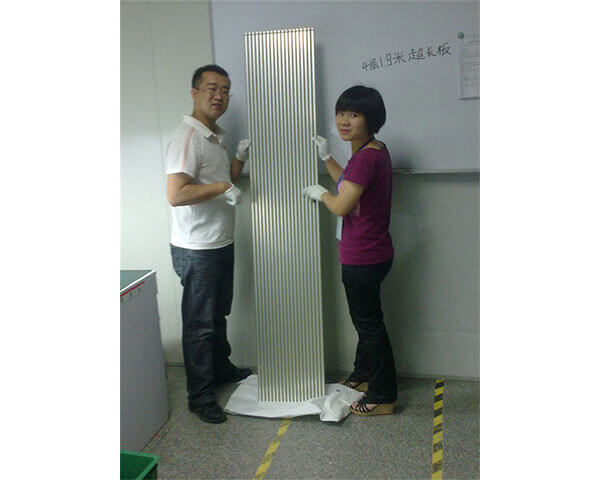
1. Used on the internal and external layers of a printed circuit board, Heavy copper PCB is accepted if it the copper is 3 ounces ft2 to 10 oz per ft2 in the outer and inner layers.
2. Heavy Copper Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a combination of processes that allows extreme copper thickness requirements to become efficient and cost effective. This process uses heavy base copper that delivers consistent and reliable high power circuits.
3. Improved copper balances substrate into the holes by changing a weak board into the long-lasting and dependable wiring platform.
4. You should always check the copper’s thickness during the circuit design stage, heavy copper conductor increases the entire thickness of PCB.
5. The capability of heavy copper helps to survive frequent exposure of excessive current, elevated temperatures and recurring thermal cycling that can destroy a regular circuit board in seconds.
6. The high tolerance capacity of heavy copper makes it compatible with applications in rough situations such as, defense and aerospace industry products.
7. Compact in product size as the several copper weights are used in the same layer of circuitry.
8. To add to the thickness of the copper to planes, traces, pads and plated-through-holes, the Laminated Deposition circuits are plated. Circuit layers are then laminated using an epoxy-based substrate such as FR4 or polyimide while in the making of Heavy copper PCB.
9. The increasing demand for heavy copper-clad boards is extraordinary especially in computer, military, automotive, and industrial controls in power supplies, power converters, power distribution, welding equipment, automotive industry and solar panel manufacturers, etc.
10. High copper PCB is much more costly to produce than the PCBs due to the unique design. Thus, the more complicated the design, the more it will cost to produce a heavy copper PCB.