Have you ever wondered what powers the heart of your smartphone or what’s behind the scenes of your sleek laptop? The answer lies in a technology so vital yet so overlooked: the Thin PCB (Printed Circuit Board). In this article, we’re unraveling the mystery of Thin PCB Boards, making it as easy to understand as your morning coffee. So, let’s dive in and discover the marvels of these technological wonders together!
What is a Thin PCB Board?
Imagine a spider web, intricate and precise, connecting different points with a purpose. That’s what a Thin PCB Board is like at the heart of your electronic devices. It’s a platform for connecting various electronic components in a compact, efficient, and reliable manner. The ‘thin’ aspect refers to its slim profile, which is essential for modern devices that demand minimalism without compromising on functionality.
The Evolution of PCB Technology
From the bulky radios of the 1950s to today’s wearable devices, PCB technology has undergone a significant transformation. The journey from using hand-drawn circuitry to employing sophisticated software for designing these boards shows how innovation has been pivotal in catering to the evolving demands of electronics.
Importance of Thin PCBs in Modern Tech
In an era where the mantra is “smaller, faster, smarter,” Thin PCBs are the unsung heroes. They enable the production of slim smartphones, drones, flexible wearables, and even medical devices that can navigate the complexities of the human body.
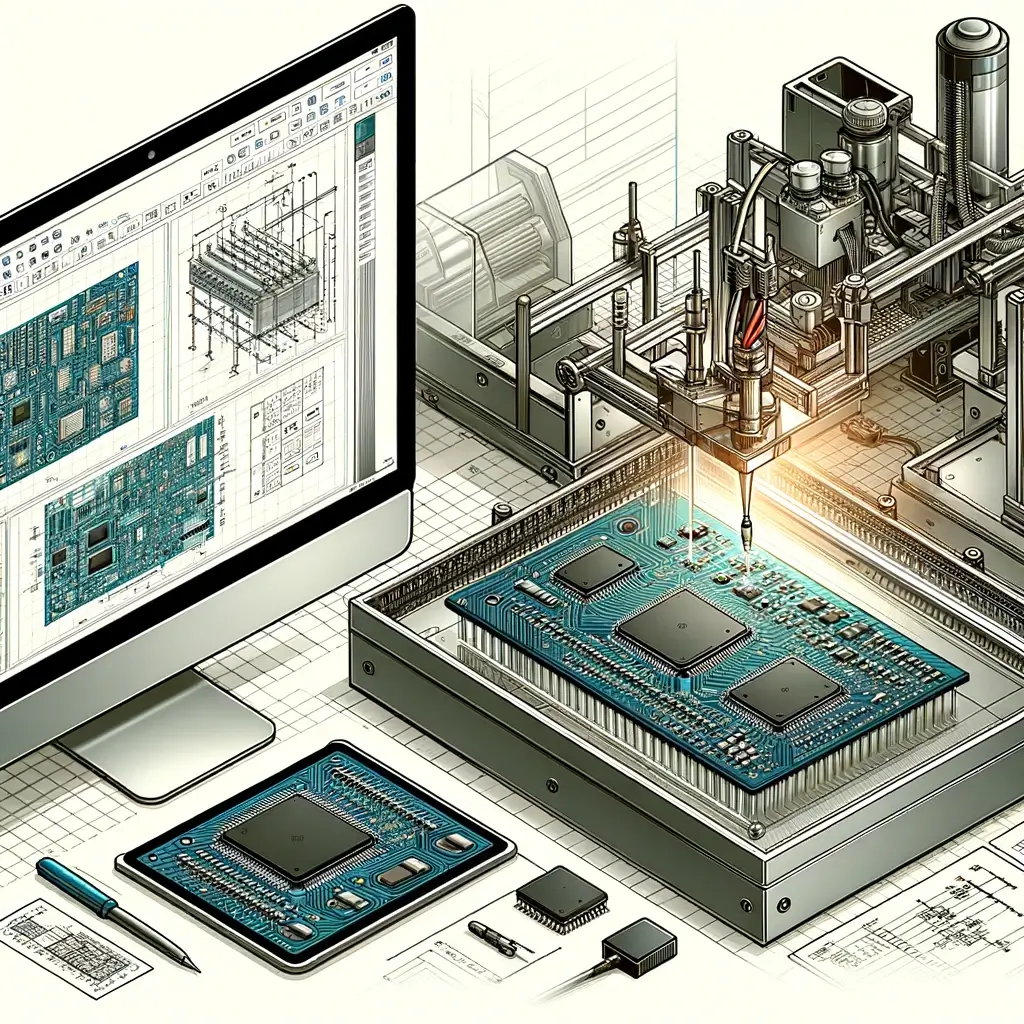
How Thin PCBs are Made
Creating a Thin PCB is akin to a chef preparing a delicate pastry, requiring precision, expertise, and the right ingredients. It involves several stages, including design, material selection, etching, and testing, to ensure that the final product is not just thin but also robust and efficient.
Types of Thin PCBs
There’s a variety to suit every need, from single-sided boards for simple devices to complex multi-layered boards that power sophisticated machinery. Each type serves a specific purpose, tailored to the demands of the device it’s designed for.
Applications of Thin PCBs
Thin PCBs are everywhere, from your pocket-sized gadgets to the Mars Rover exploring the red sands of the Martian surface. They are crucial in telecommunications, automotive industries, healthcare, and even in the realm of renewable energy.
Challenges in Designing Thin PCBs
Designing these marvels is not without its hurdles. Challenges include managing heat dissipation, ensuring signal integrity, and achieving durability, all while keeping the board as thin as possible.
Future Trends in Thin PCB Technology
As we look ahead, the future holds promising advancements, including more environmentally friendly materials, further miniaturization, and the integration of AI to make PCBs even smarter.
Choosing the Right Thin PCB for Your Needs
It’s about finding the perfect match. Factors such as the device’s application, durability requirements, and cost all play a crucial role in selecting the ideal Thin PCB.
Conclusion
The world of Thin PCB Boards is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of technological advancement. As we’ve journeyed through their significance, creation, and applications, it’s clear that these thin marvels are foundational to our digital age.
FAQs
1. What makes a PCB ‘thin’?
Thin PCBs typically have a thickness of around 0.2mm to 0.4mm, though this can vary based on the application and manufacturing technology.
2. Can Thin PCBs be repaired if they get damaged?
Yes, depending on the extent of the damage, Thin PCBs can often be repaired by skilled technicians using specialized tools and techniques.
3. Are Thin PCBs expensive?
The cost of Thin PCBs varies depending on the complexity and type. Generally, as technology advances, the cost of producing Thin PCBs decreases.
4. How do Thin PCBs impact the environment?
Like all electronic components, Thin PCBs pose environmental challenges, particularly in disposal. However, advancements in recycling technologies and the use of greener materials are helping to mitigate these impacts.
5. Can Thin PCBs be used in high-temperature environments?
Thin PCBs can be designed to withstand high temperatures by selecting appropriate materials and design techniques, although this can present additional challenges during the manufacturing process.